
A new research paper related to:
#33 – Post-Earnings Announcement Effect
Authors: Sojka
Title: 50 Years in PEAD Research
Link: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3281679
Abstract:
Analysing earning’s predictive power on stock returns was in the heart of academic research since late 60’s. First introduced to academic world in 1967 during seminar “Analysis of Security Prices” by Chicago University Professors Ray Ball and Philip Brown. In the next four decades was extensively analysed by many academics and is now a well-documented anomaly and is referred to as Post Earnings Announcement Drift (PEAD). This phenomenon is still at the centre of academic research because it stands at odds with efficient market hypothesis which assumes that all information is instantaneously reflected in stock prices. Professional investors are also closely looking at PEAD as it implies that it is easy to beat the market average by simply ranking stocks based on their earnings surprise and investing in the top decile, quintile or quartile and shorting the bottom part. Academic evidence shows that this strategy produces an abnormal return of somewhere between 2.6% and 9.37% per quarter, according to various authors. In this paper I will present existing evidence supporting and contradicting “PEAD”, the history of academic research in that field and various techniques used to verify the phenomenon. The paper is organised as follows: first the history of the PEAD academic research is presented, in the second more recent evidence and research techniques used by authors are presented and finally conclusions and various critics of PEAD are shown.
Notable quotations from the academic research paper:
“Post Earnings Announcement Drift is a measure of markets inability to price correctly information contained in earnings report. Since it was first spotted by Ball and Brown (1968), it went through rigorous academic scrutiny, first to test if it really exists (Ball (1978), Latane and Jones (1977)), then to measure its magnitude in various time frames, to offer explanations for its existence and find more PEAD variations. On average academics found that the postponed response to earnings information produces about 6% abnormal 60 days return (Dechow et al (2013)). The whole market reaction attributed to earnings report, measured from 60 days prior to earnings release to 60 days after is estimated at 18%, which means that about a third of the whole market response is delayed – Dechow et al (2013).
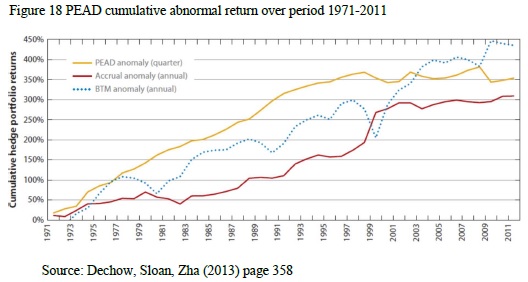
Figure 18 presents cumulative PEAD strategy abnormal returns for a 40-years period from 1971 to 2011. The total abnormal return of the strategy is an astonishing 350%, which is beat only by BTM (Book-to-Market) strategy. PEAD profits are very consistent up to late 90’s, then we can observe dips in the abnormal returns during internet bubble (1991-2001) and then during market recovery after 2008 crash. Since the middle of the 90’s PEAD returns became riskier and much lower than in the previous 25 years, it may be attributed to wider academic research in the field and wider recognition of the phenomenon among investors.
The PEAD strategy is not easy to implement in practice as it requires large scale data collection and data processing, more recent advancements in information processing technologies may also affect the magnitude of PEAD exploitation. A dominant part of research on PEAD was conducted in the US and based on US stock market data. The magnitude of PEAD computed by academics across time, since 1968 when first academic paper mentioning PEAD was published, up to the most recent evidence, are shown in Table 26.
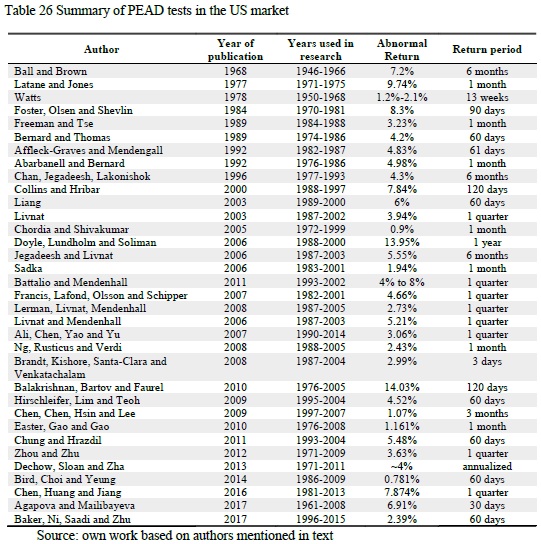
PEAD premium computed based on US market data by academics is not easily comparable. There are differences in period studied, subset of stocks used, definitions of expected earnings or unexpected earnings signal altogether. Among the results presented in Table 26, the highest return 14.03% in 120 days presented by Balakrishnan et al (2009) and the lowest is Chordia and Shivakumar (2005) 0.9% in 1 month. Both of those research papers confirm PEAD premium existence, but Chordia and Shivakumar (2005) focus their attention on explaining joint anomalies of momentum and PEAD, and form portfolios each month regardless of profit announcement date, taking last announced earnings in their SUE ranking, which obviously weakens the earnings signal.
Are you looking for more strategies to read about? Sign up for our newsletter or visit our Blog or Screener.
Do you want to learn more about Quantpedia Premium service? Check how Quantpedia works, our mission and Premium pricing offer.
Do you want to learn more about Quantpedia Pro service? Check its description, watch videos, review reporting capabilities and visit our pricing offer.
Are you looking for historical data or backtesting platforms? Check our list of Algo Trading Discounts.
Or follow us on:
Facebook Group, Facebook Page, Twitter, Linkedin, Medium or Youtube
Share onLinkedInTwitterFacebookRefer to a friend
























