Everybody can see that international equity markets are highly correlated (and especially during past 10-15 years). A new interesting financial research paper shows that ETF arbitrage mechanism is one of the key channels through which U.S. shocks propagate to local economies leading to increased return correlation with the U.S. market:
Authors: Filippou, Gozluklu, Rozental
Title: ETF Arbitrage and International Correlation
Link: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3287417
Abstract:
Assets under management of exchange-traded funds (ETF) have been growing significantly, yet the majority of ETF trades still occur on U.S. exchanges. We show that investment decisions of both institutional and retail investors when trading international country ETFs are mostly driven by shocks related to U.S. fundamentals, measured by VIX, rather than local country risks. Investors react only to negative news about local economies. When U.S. economic uncertainty increases, investors leave the country ETF market and switch to Cash ETF products. We demonstrate that ETF arbitrage mechanism is one of the key channels through which U.S. shocks propagate to local economies leading to increased return correlation with the U.S. market both in time-series and cross-sectional dimensions. We find that countries with stronger ETF price-discovery and lower limits to arbitrage tend to have a higher comovement with the U.S. market.
Notable quotations from the academic research paper:
"Signi�ficant innovations in �financial products made international investments increasingly possible. Over the recent years, exchange-traded funds experienced a double-digit growth in assets under management. Nevertheless, the short-run interdependence of trading across major international ETFs and its association with local and global risk aversion remain understudied. While the majority of earlier studies focuses on direct eff�ects of ETFs on the underlying securities in the basket that it tracks, we examine the indirect e�ffect of ETF trading as a transmission mechanism of U.S. market shocks to foreign country equity markets.
We provide a view that as the U.S. accommodates the largest share of ETF global trading volume, its market conditions directly impact the decisions of country ETF investors. We show that international ETF market participants trade based on shocks related to U.S. fundamentals rather than local ones, and propagate those shocks to local markets. The shock transmission is performed via ETF arbitrage. We argue that such arbitrage activity is one of the few mechanisms responsible for increasing correlation between the U.S. market and the rest of the world.
This high cross-country correlation limits the ability of investors to cheaply diversify U.S. risk via international ETF investments. In addition, ETFs often provide an easier access to less integrated emerging markets or to countries were direct investments are costly (e.g., Brazil). However, the transmission of U.S. shocks to those markets limits the diversi�fication bene�ts of emerging market strategies.
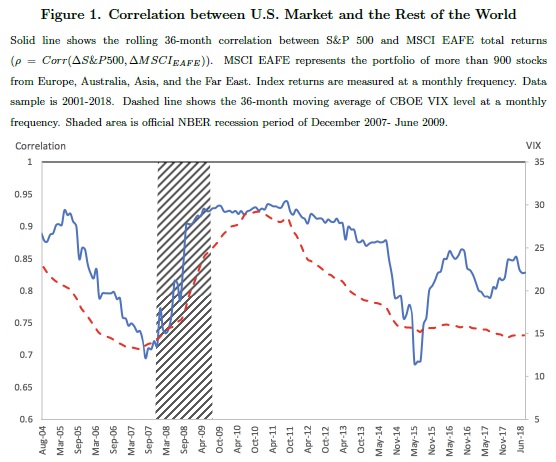
We fi�rst test the hypothesis whether country ETF investors react to changes in the U.S. rather than local economic uncertainty, as measured by CBOE Volatility Index (VIX). To this end, we compute order imbalances of retail investors (e.g., Boehmer, Jones, and Zhang, 2017), and trades of di�fferent size, capturing high frequency trading (HFT) and institutional trades. Focusing on a large cross-section of 41 countries, we �find strong association between ETF order imbalances and U.S. VIX, indicating that international investment decisions are mainly driven by the latter measure, rather than its local counterparts. For example, an increase in the U.S. VIX results in a selling pressure in the country ETF market. Such result is robust to di�fferent volatility regimes and is consistent across di�fferent types of investors. Asymmetric response analysis confi�rms that country ETF investors only react to positive changes in local VIX, which correspond to negative news in the local markets. Moreover, we observe that, when reacting to an increase in U.S. uncertainty, investors switch to safer assets such as cash equivalent ETFs. We also �find that investors respond to changes in U.S. political uncertainty di�fferently than to economic uncertainty – they leave the U.S. stock market and buy international country-level ETFs. However, they do not react to local political uncertainty and the economic eff�ect of political risk is much smaller than of changes in U.S. VIX.
In order to access the impact of ETF arbitrage on correlation of country returns with the U.S. market, we regress daily innovations in such correlation on a proxy for ETF arbitrage during di�fferent volatility regimes. We provide time-series evidence that during periods of high volatility in the U.S., an increase in the arbitrage activity by the authorized participant (AP) (as measured by net share creation/redemption) results in an increase in innovation in such daily correlation. We argue that during periods of high volatility in the U.S. market, it is harder for investors to distinguish between noise and fundamental component of the order flow. Consequently, based on wake-up call hypothesis investor may treat U.S. shocks as relevant to their own country and consume such shocks via ETF arbitrage.
We also explain cross-country variation in return correlation with the U.S. market. According to Ben-David, Franzoni, and Moussawi (2018), non-fundamental shocks must be reversed over time. This suggests that if all shocks transmitted from ETF market to local economies were non-fundamental, ETF arbitrage would not contribute towards increased correlation. In contrast, if the price deviation from the NAV is due to faster incorporation of fundamental information in ETF market, then arbitrage should a�ffect returns of underlying index, and such e�ffect should not be reverted. If such fundamental information is common both to U.S. and local market, one should observe a higher correlation between them.
Consistent with the literature, we argue that ETF transmits both fundamental and noise shocks to the underlying economies. We show that countries that have a higher degree of price discovery in their ETFs have on average a higher correlation with the U.S. market. In these markets fundamental information gets incorporated into ETF prices faster than in the Net Asset Value (NAV), and therefore, market makers closely follow and learn from changes in ETF prices. This is the case when derivative securities price the underlying assets, rather than the other way around. In addition, in order for fundamental shocks to get transmitted to underlying markets, the authorised participants (AP) must engage in arbitrage activity. We �find that the lower the limits to ETF arbitrage the higher is the correlation between a country and the U.S. market. Neither the international trade channel nor the business cycles alter this result."
Are you looking for more strategies to read about? Check http://quantpedia.com/Screener
Do you want to see an overview of our database of trading strategies? Check https://quantpedia.com/Chart
Do you want to know how we are searching new strategies? Check https://quantpedia.com/Home/How
Do you want to know more about us? Check http://quantpedia.com/Home/About
Follow us on:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/quantpedia/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/quantpedia


 "
" "
"
 "
"





